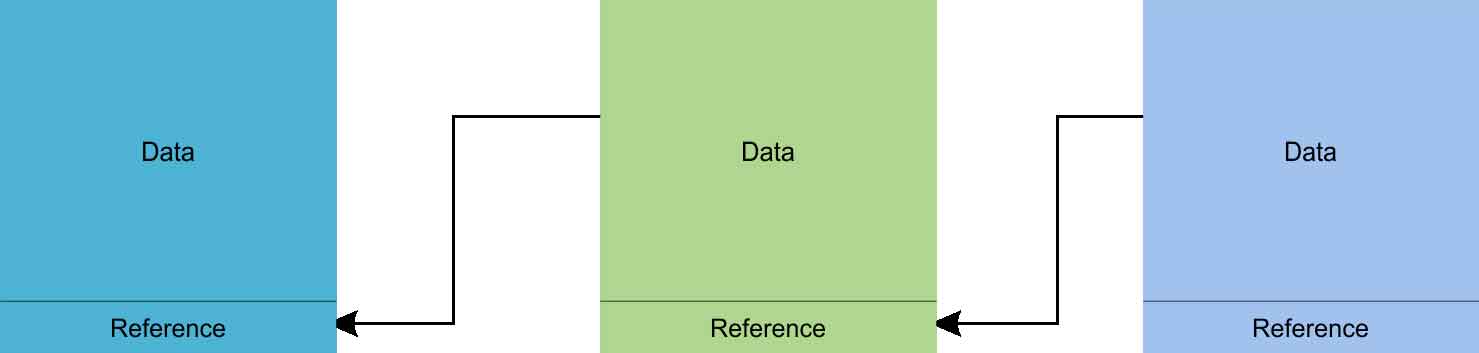
A blockchain basically means a distributed ledger system in which the data is distributed among the multiple nodes.
It is similar to linked-list data structure in that the hash-value of the previous block is getting stored in the next block and the new node gets appended and thus forms a chain. Apart from the hash-value of the previous block it also stores the data and timestamp.
The term blockchain becomes popular because of the term “Immutability” that is once the data gets stored in the block no one can tempered or alter the data at any cost. This is because the hash-value of the current block is stored in the next block and if we try to manipulate the data the hash value of the block changes and thus, we lose the whole chain.
Features of a Blockchain:
Immutability:
Blockchain has become very popular because of its various features but “Immutability” is considered as one of the important features in the blockchain technology. The term Immutability means something that cannot be changed or altered. Once the data is stored in the block no one can tempered or manipulate the data. Hence the Integrity of the data is maintained in the blockchain technology.
Decentralized:
The term decentralized in the blockchain means it does not have any governing authority or a single entity who can run the network; rather a group of each individual node maintains the network by using the terminology “Consensus Protocol” and thus makes the network decentralized.
As we know that the blockchain is a public network so anyone from anywhere can join the network. Let's make it simpler. Blockchain puts us as a user. So as in the network no single entity owns the whole responsibility of the system, we can directly access it from anywhere and store our assets there.
We can store anything including the cryptocurrencies, important documents, contracts or other important digital assets. And with the help of blockchain, you will have full control over them using your private key and no one can temper or manipulate your data hence integrity of our documents and valuable assets is maintained in the blockchain.
Distributed Ledger:
In the blockchain network the data is being distributed among the various nodes in the network hence this feature also makes the blockchain technology very powerful.
Basically, a public ledger provides all the necessary information about all the transactions and the participants. It is all out in the open and everyone in the network can see the data, nowhere to hide. Although the case for private or consortium blockchain is a bit different. But still many participants are able to see what really happens in the ledger.
This happens because the ledger on the network is maintained by all other participants in the network. This distributed computational power across the computers helps for a better outcome.
This is the reason why it is considered as one of the blockchain’s important features.
Consensus:
Consensus protocol is one of the key functionalities in the blockchain network. It helps the people in the network to trust each other and also helps the people to come to a certain conclusion on an agreement.
In simple words, the consensus is a decision-making process for the group of nodes active in the network. Here, the nodes can come to a certain agreement quickly and relatively faster and thus makes the decision making much faster for the network. When all of the nodes are validating a transaction, a consensus is absolutely necessary for a system to run smoothly. We could think of it as similar to a voting system, where the majority wins, and the minority has to support them.
The consensus is responsible for the network being trustworthy. Nodes in a network may not trust each other, but they can trust the algorithms that run at the core of it. That is why every decision on the network is a winning scenario for the blockchain.
There are various consensus algorithms for blockchains available over the globe such as Proof of Work (POW), Proof of Stake (POS), Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) etc. Each one has its own unique way to make decisions and perfecting previously introduced mistakes. The architecture creates a realm of fairness on the web.
Types of Blockchains:
Public blockchain:
A public blockchain has no access restrictions. Anyone from anywhere with an internet connection can join the network and can send transactions to it as well as become a validator (i.e., participate in the execution of a consensus protocol). Usually, such networks offer economic incentives for those who secure them and utilize some type of a proof of stake or proof of work algorithm.
One of the largest and most known public blockchains are the bitcoin blockchain (Satoshi Nakamoto) and the Ethereum blockchain (Vitalik Buterin).
Private blockchain:
A private blockchain is a permissioned one. No one can join it unless invited by the network administrators. Participant and validator access is restricted in the network. To differentiate between open blockchains and other peer-to-peer decentralized database applications that are not open ad-hoc compute clusters, the terminology distributed ledger is normally used for the private blockchains.
Hybrid blockchain:
It is a special type of blockchain technology that combines the properties of both private and public blockchain. It helps organizations to set up a private or permission-based system along with a public permissionless system, allowing them to control who can access the specific data stored in the blockchain ledger, and which type of data will be opened up publicly for all.
federated blockchain:
The fourth type of blockchain is federated blockchain, also known as a consortium blockchain. It is the same as a hybrid blockchain. It supports private and public blockchain features. But it is different in that multiple organizational members work on a decentralized network. Basically, a federated blockchain is a private blockchain with the restricted access to a particular group and has restrictions on the other activities, this is because of terminating the risks that come with a single person who controls the network on a private blockchain.
Future Scope:
Blockchain in digital Financial Sector:
blockchain can play a vital role in financial sector it will support cross border transactions that is transferring the money across the money is comparatively slow and expensive but blockchain can be accurate and very much less expensive. Apart from this blockchain can also be helpful in clearing and settlement, digital identity verification etc
Blockchain in supply chain management:
A blockchain supply chain system can help individuals to record price, date of manufacturing, exact location, quality of their goods and other relevant information to more efficiently manage the supply chain system. The availability of this information within blockchain can increase traceability of material supply chain, improve visibility and compliance over outsourced contract manufacturing, and potentially enhance an organization's position as a leader in responsible manufacturing.
Blockchain in Healthcare Industry:
Blockchain can play a significant role in the healthcare industry. The blockchain technology ensures the secure transfer of medical records of patients, manages the medicine supply chain and helps healthcare researchers to grab genetic code.
Healthcare is one of the data-insufficient sectors in India. A lot of time is being wasted in the compilation of various details related to patients which must be rather spent on providing medical facilities to those who are in dire need of them.